Navigating the Future of Healthcare: The Impact of Telemedicine in Developing Countries
We as humankind are now realizing the healthcare transitions as countries are advancing and technology is empowering so many more countries. For developing countries, the highlight of advancements is telemedicine for sure, a bold step towards revolutionizing how healthcare can be provided and how boundaries no longer are a barrier. Now that everyone can receive healthcare eventually transforming the industry for the future. In this blog, we shall discuss how telehealth interacts, reacts, and affects patients and healthcare workers in developing countries.
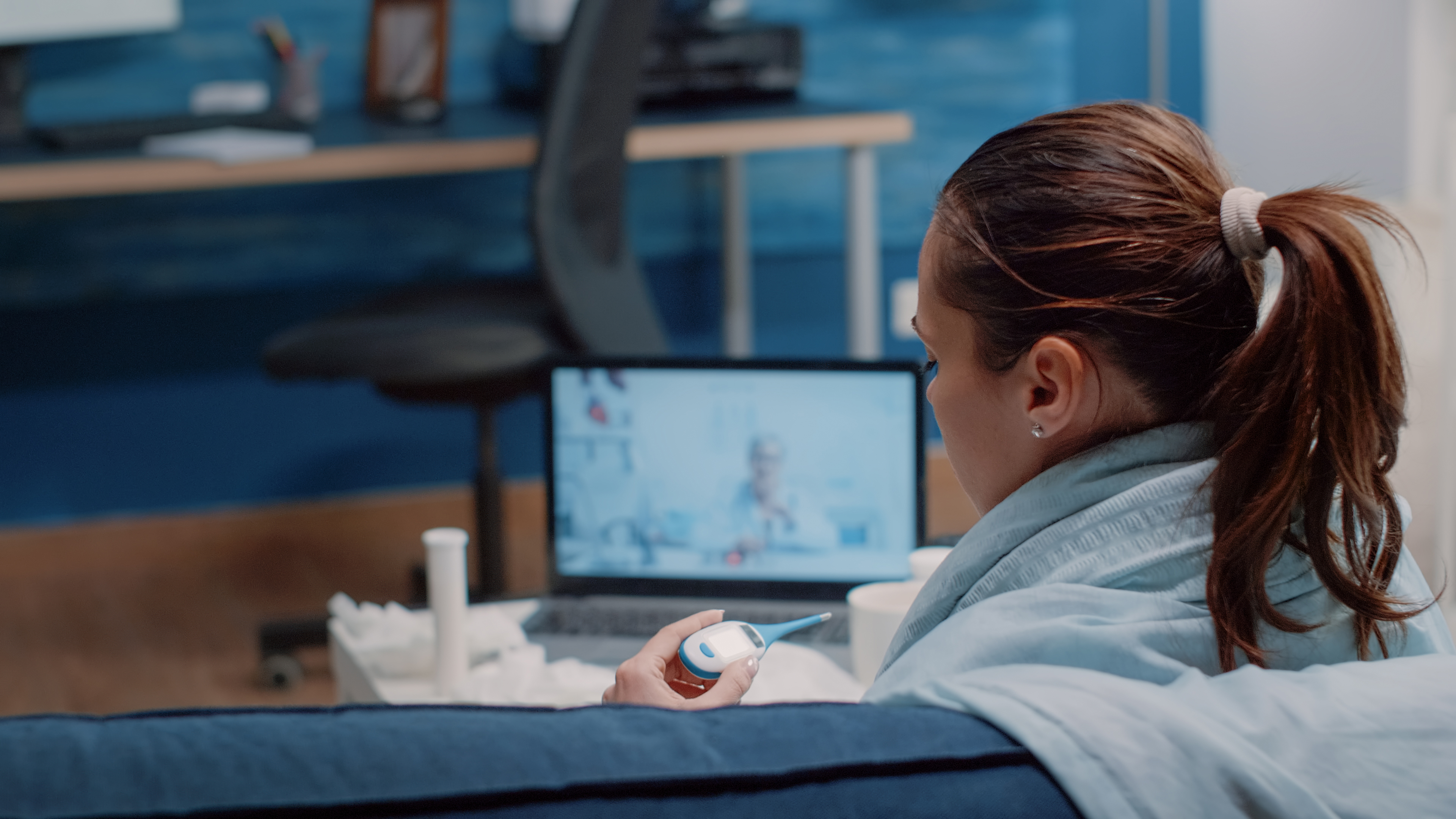
This at its simplest definition would mean…’how do I get treated without being physically there?’. Putting distance in perspective, Telemedicine encompasses anything from talking to your doctor via video to keeping track of patient data through various mobile health systems for better treatment and education. Understanding the escalation of violence and loss of goods, telehealth doesn’t just act as an alternative to those times, it completely transforms everything. It saves individuals money and time by allowing them to get medical advice without traveling far.</s>
Telemedicine has a lot of advantages, one of which is that it broadens the reach of health care services. In many rural and isolated areas, patients actively look for facilities and health care providers but are unable to find them. However, it is made possible by allowing patients to see other doctors and specialists even if they are thousands of miles apart. For example, a farmer living in a far-flung area can talk to a specialist based in another big city without moving from his place. This practice would save time and also may make it possible to reduce the time it takes to carry out important processes such as diagnosis and treatment of patients which eventually translates to better health of the patient.
What is more, telemedicine makes it easier to access care in certain areas that may be marked with stigma. In some developing countries, cultural activities may stop people from reaching out for help for mental health or sexual and reproductive health. Telemedicine to some extent, provides privacy which allows people to get the help they require. Thanks to these apps and other online platforms, patients can receive advice and help while remaining free from stigma or social backlash.
The other relevant benefit of telemedicine is cost-effectiveness. In most cases, the patients have to bear additional charges, like traveling expenses, accommodation, and even loss of pay because of taking leave from work. Telemedicine has the capacity to minimize these expenses comprehensively. For example, a patient doesn’t have to travel in order to have a consultation and there is also no set of costs associated with it. In a society where every dollar is precious, this can be of great help to families trying to get by.
Similarly, healthcare providers in developing nations are also reaping the benefits of the adaptation of telemedicine in their practice. Thanks to technology, doctors are able to cater for many patients at a go, which in turn leads to shorter waiting periods and provision of better care to the patients. Telemedicine services also allow for easy and constant education, and training of the medical care provides on the new medical technologies and the best practices in medicine s. This is especially relevant in areas where access to education and resources is challenging.
While there are numerous advantages, the integration of telemedicine in developing nations is not without its problems. One major issue is the ‘digital divide’. Though the use of mobile phones is extensive, there is often a lack of steady internet services, especially in the countryside. In order to fully harness the potential of telemedicine, governments and other organizations should focus on investing to enhance the digital backbone and ensuring that everyone is able to access the relevant equipment.
Another key barrier relating to telemedicine is technology and data privacy. With information on patients being more dependent on the storing and sharing by technology-issues such as ensuring that data is not violated or hacked becomes highly important. Developing countries need to invest in the development of sound laws and security protocols to enhance protection of patients’ data.
In addition, there is a need to put in place legal systems that will enable the practice of telemedicine. Many developing nations have telemedicine policies; this can lead to difficulty to both caregivers and patients. Clear legal instruments will ensure the telemedicine is enhanced and many patients who have been reluctant to adopt this mode of treatment will gain confidence and be able to utilize these services.
To summarize, telmedicine is expected to change the narrative of healthcare services in developing nations by addressing increasing accessibility, reducing costs, and enhancing patient outcomes. Despite the presence of a few hurdles to cross the likely potenential is significant. As we move forward into the rest of the healthcare future, it is crucial that governments, healthcare providers and technology developers effectively come together and develop an ecosystem conducive for proliferation of telemedicine. This way we can guarantee that millions of people in the developing low-income countries get the treatment they are supposed to get thus bettering the entire society and the future.



